Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers.
Identification—
A:
Dissolve 30 mg of Atropine and 36 mg of
USP Atropine Sulfate RS in individual 60-mL separators with the aid of 5-mL portions of water. To each separator add 1.5 mL of 1 N sodium hydroxide solution and 10 mL of chloroform. Shake for 1 minute, allow the layers to separate, and filter the chloroform extracts through separate filters of about 2 g of anhydrous granular sodium sulfate supported on pledgets of glass wool. Extract each aqueous layer with two additional 10-mL portions of chloroform, filtering and combining with the respective main extracts. Evaporate the chloroform solutions under reduced pressure to dryness, and dissolve each residue in 10 mL of carbon disulfide: the IR absorption spectrum, determined in a 1-mm cell, of the solution obtained from the test specimen exhibits maxima only at the same wavelengths as that of the solution obtained from the Reference Standard.
B:
To a 1 in 50 solution in 3 N hydrochloric acid add
gold chloride TS: a lusterless precipitate is formed (
distinction from hyoscyamine,
which,
similarly treated,
yields a lustrous precipitate).
Angular rotation  781A
781A :
:
the angular rotation of this solution, a 200-mm tube being used, is between
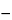
0.70

and +0.05

(limit of hyoscyamine).
Test solution—
Dissolve 1 g, previously dried at 105

for 1 hour, in sufficient 50% alcohol (w/w) to obtain a volume of 20 mL at 25

.
Readily carbonizable substances  271
271 —
—
Dissolve 200 mg in 5 mL of 2 N sulfuric acid: the solution has no more color than
Matching Fluid A, and the solution is colored no more than light yellow upon the addition of 0.2 mL of nitric acid.
Limit of foreign alkaloids and other impurities—
Prepare a solution of Atropine in methanol containing 20 mg per mL, and, by quantitative dilution of a portion of this solution with methanol, prepare a second solution of Atropine containing 1 mg per mL. Apply 25 µL of the first (20 mg per mL) Atropine solution, 1 µL of the second (1 mg per mL) Atropine solution, and 5 µL of a methanol solution of
USP Atropine Sulfate RS containing 24 mg per mL to a suitable thin-layer chromatographic plate (see
Chromatography  621
621
) coated with a 0.5-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel. Allow the spots to dry, and develop the chromatogram in a solvent system consisting of a mixture of chloroform, acetone, and diethylamine (5:4:1) until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the developing chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow the solvent to evaporate. Locate the spots on the plate by spraying with
potassium iodoplatinate TS: the
RF value of the principal spot obtained from each test solution corresponds to that obtained from the Reference Standard solution; no secondary spot obtained from the first Atropine solution exhibits intensity equal to or greater than the principal spot obtained from the second Atropine solution (0.2%).
Organic volatile impurities, Method V  467
467 :
:
meets the requirements.
Solvent—
Use dimethyl sulfoxide.
Assay—
Dissolve about 400 mg of Atropine, accurately weighed, in 50 mL of glacial acetic acid, add 1 drop of
crystal violet TS, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS to a green endpoint. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 28.94 mg of C
17H
23NO
3.