Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed containers. Store at room temperature.
Labeling—
Where it is intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, the label states that it is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms.
Bacterial endotoxins  85
85 —
—
The level of bacterial endotoxins is such that the requirements under the relevant dosage form monograph(s) in which Ropivacaine Hydrochloride is used can be met. Where the label states that Ropivacaine Hydrochloride must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms, the level of bacterial endotoxins is such that the requirements under the relevant dosage form monograph(s) in which Ropivacaine Hydrochloride is used can be met.
Color—
Transfer an accurately weighed aliquot of Ropivacaine Hydrochloride, about 480 to 500 mg, into a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in and dilute with water to volume. Pass the solution through a 5-µm polyvinylidene filter (PVDF). Immediately measure the absorbance at 405 nm and at 436 nm, using a suitable spectrophotometer and a path length of 5 cm, and using water as the reference: the absorbance at 405 nm is not more than 0.030, and the absorbance at 436 nm is not more than 0.025.
Clarity—
Hydrazine sulfate solution—
Dissolve 1.0 g of hydrazine sulfate in water, and dilute with water to 100 mL. Allow to stand 4 to 6 hours.
Hexamethylenetetramine solution—
Transfer 2.5 g of hexamethylenetetramine to a 100-mL glass-stoppered flask, and dissolve in 25 mL of water. Do not dilute to volume.
Opalescence standard stock suspension—
To the flask containing the Hexamethylenetetramine solution, add 25.0 mL of Hydrazine sulfate solution, mix, and allow to stand for 24 hours. This suspension is stable for up to 2 months when stored in a glass container free from surface defects. The suspension must not adhere to the flask and must be well mixed before use.
Opalescence standard suspension—
Dilute 15.0 mL of the Opalescence standard stock suspension with water to 1000 mL. This suspension should be freshly prepared and may be stored for not more than 24 hours.
Reference suspension 1—
Combine 5.0 mL of the Opalescence standard suspension and 95.0 mL of water. Shake before use.
Reference suspension 2—
Combine 10.0 mL of the Opalescence standard suspension and 90.0 mL of water. Shake before use.
Test solution—
Transfer about 480 to 500 mg of Ropivacaine Hydrochloride, accurately weighed, to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Procedure—
Use identical tubes of colorless, transparent, neutral glass with a flat base and an internal diameter of 15 to 25 mm. The depth of the layer is 40 mm. Compare the solutions in diffused daylight 5 minutes after the preparation of Reference suspension 1 and Reference suspension 2, viewing vertically against a black background. The diffusion of light must be such that Reference suspension 1 can readily be distinguished from water, and Reference suspension 2 can readily be distinguished from Reference suspension 1. The Test solution is considered clear if its clarity is the same as that of water or if its opalescence is not more pronounced than that of Reference suspension 1.
Specific rotation  781S
781S :
:
Solvent—
Dissolve about 200 g of sodium hydroxide in water, and dilute with water to 1 L. Combine 20 mL of this solution and 300 mL of water in a 1-L volumetric flask. Dilute with alcohol to volume.
Test solution:
10 mg per mL, in
Solvent.
Procedure—
Obtain readings at 365 nm: between –210

and –255

.
pH  791
791 :
:
between 4.5 and 6.0, in a solution (1 in 100).
Water, Method Ia  921
921 :
:
between 5.0% and 6.0%. Perform the determination on 0.0900 to 0.1100 g of sample.
Heavy metals—
pH 3.5 Acetate Buffer and Standard Lead Solution—
Prepare as directed under
Heavy Metals  231
231 .
.
Dilute lead standard solution—
Dilute 10.0 mL of the Standard Lead Solution with water to 100 mL. Each mL of Dilute lead standard solution contains the equivalent of 1 µg of lead.
0.25 M Sodium sulfide solution—
Dissolve about 6.0 g of sodium sulfide in 40 g of glycerol, then dilute with water to 100 mL. Filter using a cotton pad, and store in a glass container protected from light.
Standard solution—
Combine 10.0 mL of the Dilute lead standard solution with 2 mL of the Test Preparation and 2 mL of pH 3.5 Acetate Buffer, and mix.
Test solution—
Combine 12 mL of the Test Preparation with 2 mL of pH 3.5 Acetate Buffer, and mix.
Blank—
Combine 10 mL of water, 2 mL of pH 3.5 Acetate Buffer, and 2 mL of the Test Preparation.
Procedure—
Transfer the Blank to a color-comparison tube. Transfer the Standard solution and the Test solution to individual color-comparison tubes each containing 1 drop of 0.25 M Sodium sulfide solution. After 1 minute, compare the colors, viewing downward over a white surface: the Standard solution shows a slight brown color compared to the Blank; and the Test solution is not darker than the Standard solution (0.001%).
Limit of ropivacaine related compound A—
Buffer solution, Mobile phase, System suitability solution, and Chromatographic system—
Prepare as directed for Related compounds.
Standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of
USP Ropivacaine Related Compound A RS in
Mobile phase, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with
Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.13 µg per mL.
Test solution—
Transfer about 100 mg of Ropivacaine Hydrochloride, accurately weighed, to a 10-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with Mobile phase to volume, and mix.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks: the signal-to-noise ratio of the principal peak in the Standard solution is at least 10; and the response for any peak corresponding to ropivacaine related compound A (2,6-dimethylaniline) in the chromatogram obtained from the Test solution is not greater than the response of the major peak in the chromatogram obtained from the Standard solution (10 µg per g).
Related compounds—
Buffer solution—
Combine 1.3 mL of sodium phosphate monobasic solution (138 g per L) and 32.5 mL of disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate solution (89 g per L), and dilute with water to 1 L. The pH of this solution is 8.0. Make adjustments if necessary.
Mobile phase—
Prepare a degassed mixture of
Buffer solution and acetonitrile (50:50). Make adjustments if necessary (see
System suitability under
Chromatography  621
621
).
Test solution—
Transfer about 27.5 mg of Ropivacaine Hydrochloride, accurately weighed, to a 10-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with Mobile phase to volume, and mix.
Dilute test solution—
Dilute 1.0 mL of the Test solution with Mobile phase to 100 mL. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution with Mobile phase to 10 mL.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 240-nm detector and a 3.9-mm × 15-cm column that contains 4-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. Check the stability of the baseline by injecting
Mobile phase. Run the chromatogram for at least 15 minutes. Chromatograph the
System suitability solution and the
Dilute test solution, and record the peak responses as directed for
Procedure: the relative retention times are 1.6 for bupivacaine and 1.0 for ropivacaine; the resolution,
R, between ropivacaine and bupivacaine is not less than 6 (from the
System suitability solution); and the signal-to-noise ratio of ropivacaine is at least 10 (from the
Dilute test solution).
Procedure—
Inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the
System suitability solution and the
Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Ropivacaine Hydrochloride taken by the formula:
100(rU / rS),
in which
rU is the peak response for each impurity obtained from the
Test solution; and
rS is the sum of all peak responses obtained from the
Test solution: not more than 0.2% of bupivacaine is found, less than 0.1% for any other individual impurity is found, and not more than 0.5% of total impurities is found.
Enantiomeric purity—
Background electrolyte solution—
Transfer 9.31 to 10.29 g of phosphoric acid to a 1-L volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. The pH is between 2.9 and 3.1. If necessary, adjust the pH with triethanolamine.
Run buffer—
Prepare a solution containing approximately 13.3 mg of heptakis-(2,6-di-
O-methyl)-
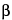
-cyclodextrin per mL of
Background electrolyte solution.
[NOTE—This solution is freshly prepared and passed through a 0.45-µm filter.
]
Test solution—
Transfer about 50 mg of Ropivacaine Hydrochloride, accurately weighed, to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in and dilute with water.
Dilute test solution—
Dilute 1.0 mL of the Test solution with water to 200 mL.
Capillary rinsing procedure—
Use separate run buffer vials for capillary rinse and sample analysis. Rinse the capillary with water for 1 minute, with 0.1 N sodium hydroxide for 10 minutes, and with water for 3 minutes. If a new or dry capillary is being used, increase the sodium hydroxide rinse time to 30 minutes. Rinse the capillary between injections as follows: water for 1 minute, 0.1 N sodium hydroxide for 4 minutes, and water for 1 minute, then run buffer for 4 minutes. Rinse times are based on a rinse pressure of 1 bar.
System setup (see Capillary Electrophoresis  727
727 )—
)—
The system is equipped with a 206-nm detector and a 50-µm × 72-cm fused silica column. The temperature is maintained at 30

. A voltage of 375 V/cm is applied. The initial ramping is 500 V/s, positive polarity, and a resulting current of 40 to 45 µA. Inject the
Dilute test solution: the signal-to-noise ratio is at least 10. Inject the
System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for
Procedure: the relative migration times are about 0.96 for ropivacaine related compound B (
R enantiomer) and 1.0 for ropivacaine (
S enantiomer); the resolution,
R, between ropivacaine related compound B and ropivacaine is not less than 3.7. The analysis run time is about 30 minutes. If needed, increase the resolution by increasing the concentration of heptakis-(2,6-di-
O-methyl)-
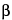
-cyclodextrin or by lowering the system temperature.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes of the
Run buffer and of water to ensure there are no interfering peaks (50 mbar for 5.0 seconds followed by injection of
Run buffer at 50 mbar for 1.0 second). Inject the
Test solution into the electrophoresis system, record the electropherograms, and measure the peak responses for ropivacaine and ropivacaine related compound B. Calculate the percentage of ropivacaine related compound B in the portion of Ropivacaine Hydrochloride taken by the formula:
100(rR / MR)/(rS / MS),
in which
rR is the peak response of ropivacaine related compound B obtained from the
Test solution; rS is the peak response of ropivacaine obtained from the
Test solution; and
MR and
MS are the migration times, in minutes, of ropivacaine related compound B and ropivacaine, respectively: not more than 0.5% ropivacaine related compound B is found.
System shutdown—
After the analysis, rinse the capillary for 10 minutes with 0.1 N sodium hydroxide, then for 10 minutes with water. Dry the capillary before storage.
Other requirements—
Where the label states that Ropivacaine Hydrochloride is sterile, it meets the requirements for
Sterility Tests  71
71
and
Labeling under
Injections  1
1
.
Assay—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of Ropivacaine Hydrochloride, approximately 1000 mg, in 10 mL of water and 40 mL of alcohol. Add 1.0 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid, and titrate with 1 N sodium hydroxide VS. Two equivalence points are obtained; the difference in titrant volume corresponds to the amount of ropivacaine hydrochloride. Each mL of 1 N sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 310.9 mg of anhydrous ropivacaine hydrochloride (C17H26N2O·HCl).